Strategic Management:
An Overview
Strategic Management is a comprehensive approach to setting goals, planning, and guiding an organization's actions towards achieving long-term objectives. It integrates various functions and activities within the organization to ensure cohesive movement toward the set goals.
Key Components of Strategic Management
-
Strategic Analysis:
- Internal Analysis: Assessing the organization's internal environment to identify strengths and weaknesses (e.g., resources, capabilities, core competencies).
- External Analysis: Examining external factors such as market trends, competition, economic conditions, and regulatory environments (using tools like PESTEL analysis and Porter's Five Forces).
-
Strategy Formulation:
- Vision and Mission Statements: Defining the organization's purpose, values, and long-term aspirations.
- Setting Objectives: Establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
- Developing Strategies: Crafting strategies at various levels (corporate, business, and functional) to achieve the objectives.
-
Strategy Implementation:
- Resource Allocation: Distributing resources effectively to support the strategies.
- Organizational Structure: Designing the organizational structure to facilitate efficient strategy execution.
- Change Management: Managing the process of change within the organization to align with strategic goals.
-
Strategy Evaluation and Control:
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly reviewing and assessing performance against strategic goals using key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Feedback and Adjustment: Making necessary adjustments to strategies based on performance data and changing external conditions.
Importance of Strategic Management
-
Direction and Focus:
- Provides a clear direction and focus for the organization, aligning all activities and resources towards common goals.
-
Competitive Advantage:
- Helps in identifying and developing unique strengths and capabilities that give the organization a competitive edge.
-
Adaptability and Resilience:
- Enables the organization to anticipate and respond to changes in the external environment, enhancing its adaptability and resilience.
-
Resource Optimization:
- Ensures optimal allocation and utilization of resources, leading to increased efficiency and effectiveness.
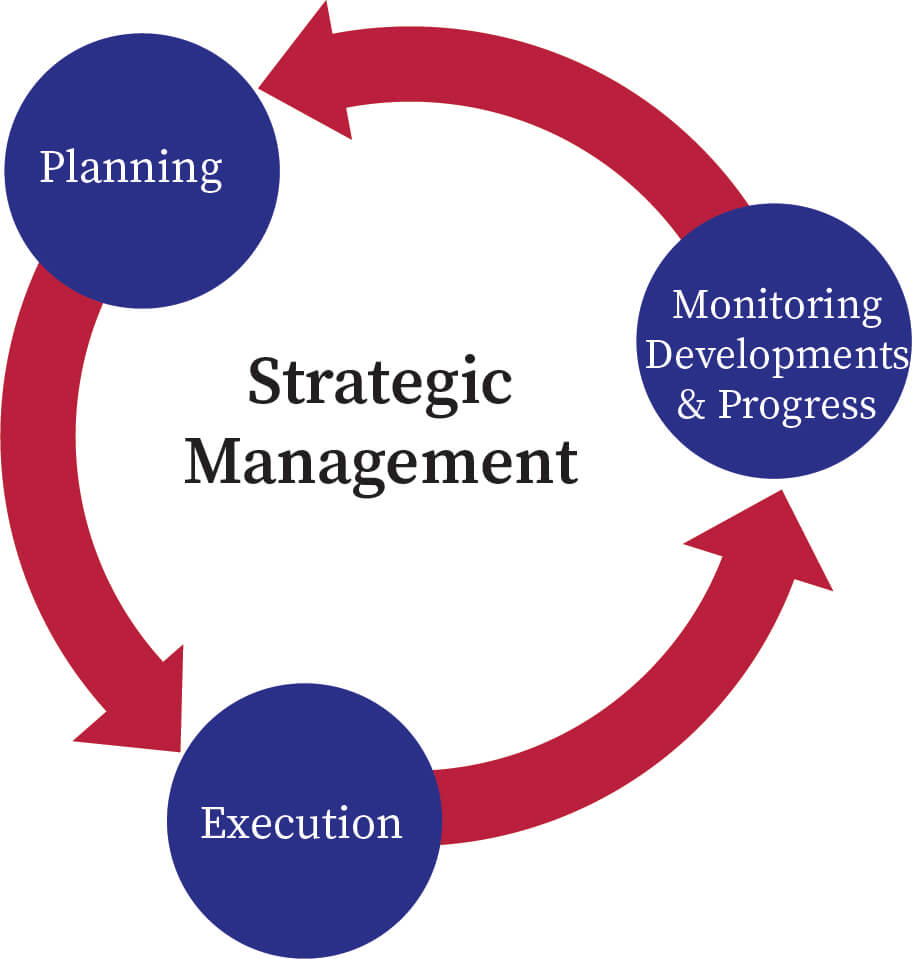
Strategic Management Process
- Environmental Scanning:
- Conducting a thorough analysis of internal and external environments to identify opportunities and threats.
- Strategy Development:
- Formulating strategies that leverage the organization's strengths and address its weaknesses while capitalizing on opportunities and mitigating threats.
- Implementation Planning:
- Developing detailed plans and initiatives to implement the chosen strategies, including timelines, responsibilities, and resource requirements.
- Execution:
- Carrying out the implementation plans, ensuring all parts of the organization are working in sync towards the strategic objectives.
- Review and Control:
- Continuously monitoring progress, evaluating outcomes, and making necessary adjustments to stay on track with strategic goals.
Examples of Strategic Management Models
- SWOT Analysis:
- A tool for identifying the organization's internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats.
- Balanced Scorecard:
- A performance management tool that views the organization from four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
- Porter's Five Forces:
- A framework for analyzing the competitive forces within an industry to understand the intensity of competition and profitability potential.
Challenges in Strategic Management
- Dynamic Environments:
- Rapid changes in technology, market conditions, and regulations can make it challenging to stay aligned with strategic goals.
- Resource Constraints:
- Limited resources can hinder the effective implementation of strategies.
- Resistance to Change:
- Employees and stakeholders may resist changes necessary for strategic initiatives, requiring effective change management practices.
Conclusion
Strategic management is essential for organizations to achieve their long-term goals and maintain a competitive advantage. By integrating strategic analysis, formulation, implementation, and evaluation, organizations can navigate complex environments and drive sustainable growth.
keep reading and growing. good Luck !