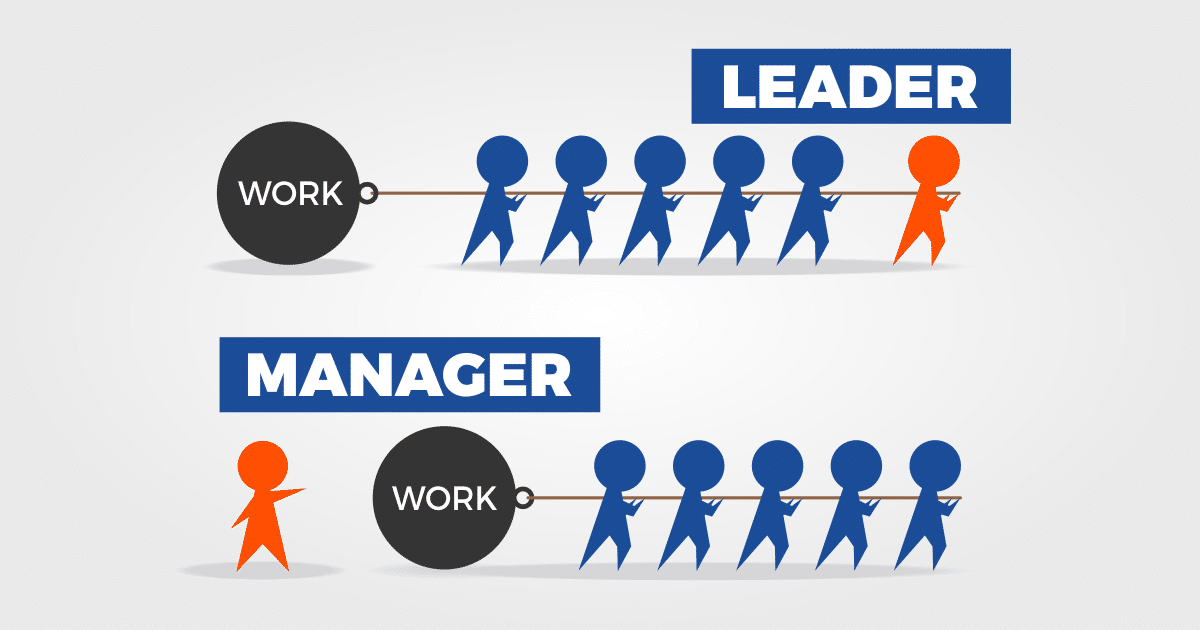
Manager vs. Leader: Key Differences and Overlaps
Managers and leaders both play critical roles in organizations, but their functions, approaches, and impacts often differ. Understanding these distinctions can help individuals develop a balanced skill set to effectively guide their teams and achieve organizational goals.
Key Differences
-
Focus and Objectives:
- Manager: Primarily focused on achieving organizational goals through planning, organizing, and controlling resources. Managers emphasize efficiency, stability, and consistency.
- Leader: Focuses on setting a vision, inspiring, and motivating people. Leaders emphasize innovation, change, and the personal growth of team members.
-
Approach:
- Manager: Utilizes formal authority and relies on established processes, rules, and policies. Management is often task-oriented.
- Leader: Relies on influence and inspiration rather than formal authority. Leadership is people-oriented and focuses on building relationships and trust.
-
Decision-Making:
- Manager: Tends to make decisions based on analysis, data, and established protocols. The decision-making process is often systematic and procedural.
- Leader: Makes decisions that align with the broader vision and goals. Leaders may take calculated risks and are often more intuitive and innovative in their decision-making.
-
Change Management:
- Manager: Aims to maintain order and consistency, managing change in a controlled manner. Managers implement change through structured plans.
- Leader: Acts as a change agent, encouraging and driving innovation and transformation. Leaders inspire others to embrace and adapt to change.
-
Time Orientation:
- Manager: Focuses on short-term goals and immediate results, ensuring that daily operations run smoothly.
- Leader: Looks at the long-term vision and strategic direction, aiming for future growth and development.
Overlapping Qualities
While there are distinct differences, managers and leaders share overlapping qualities, and effective individuals often exhibit both sets of characteristics.
-
Communication Skills:
- Both managers and leaders must communicate effectively to convey their vision, goals, and expectations to their teams.
-
Motivation:
- Managers motivate employees through rewards, recognition, and performance management, while leaders inspire through vision and personal example.
-
Problem-Solving:
- Both roles require strong problem-solving skills, whether it's managing day-to-day issues or addressing strategic challenges.
-
Accountability:
- Managers and leaders both hold themselves and their teams accountable for performance and results.
Contextual Examples
-
Manager:
- A project manager ensures that a project is completed on time, within budget, and to specification. They create detailed plans, allocate resources, and monitor progress.
-
Leader:
- A CEO sets a bold vision for the company's future, inspires employees to innovate, and drives the organization towards long-term goals.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions and overlaps between management and leadership is crucial for organizational success. Managers ensure that the organization's day-to-day operations run smoothly and efficiently, while leaders inspire and guide the organization toward a visionary future. Balancing both sets of skills can enhance overall effectiveness and drive sustained success.