Biometric Authentication Systems: Revolutionizing Security and Convenience
Introduction
In the age of digital transformation, security and convenience are paramount. Biometric authentication systems have emerged as a groundbreaking solution, offering enhanced security and user-friendly access control. This blog explores the world of biometric authentication, its technologies, applications, benefits, and future trends.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security process that verifies a user's identity based on unique biological characteristics. Unlike traditional authentication methods like passwords or PINs, biometrics rely on inherent physical or behavioral traits, making it difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
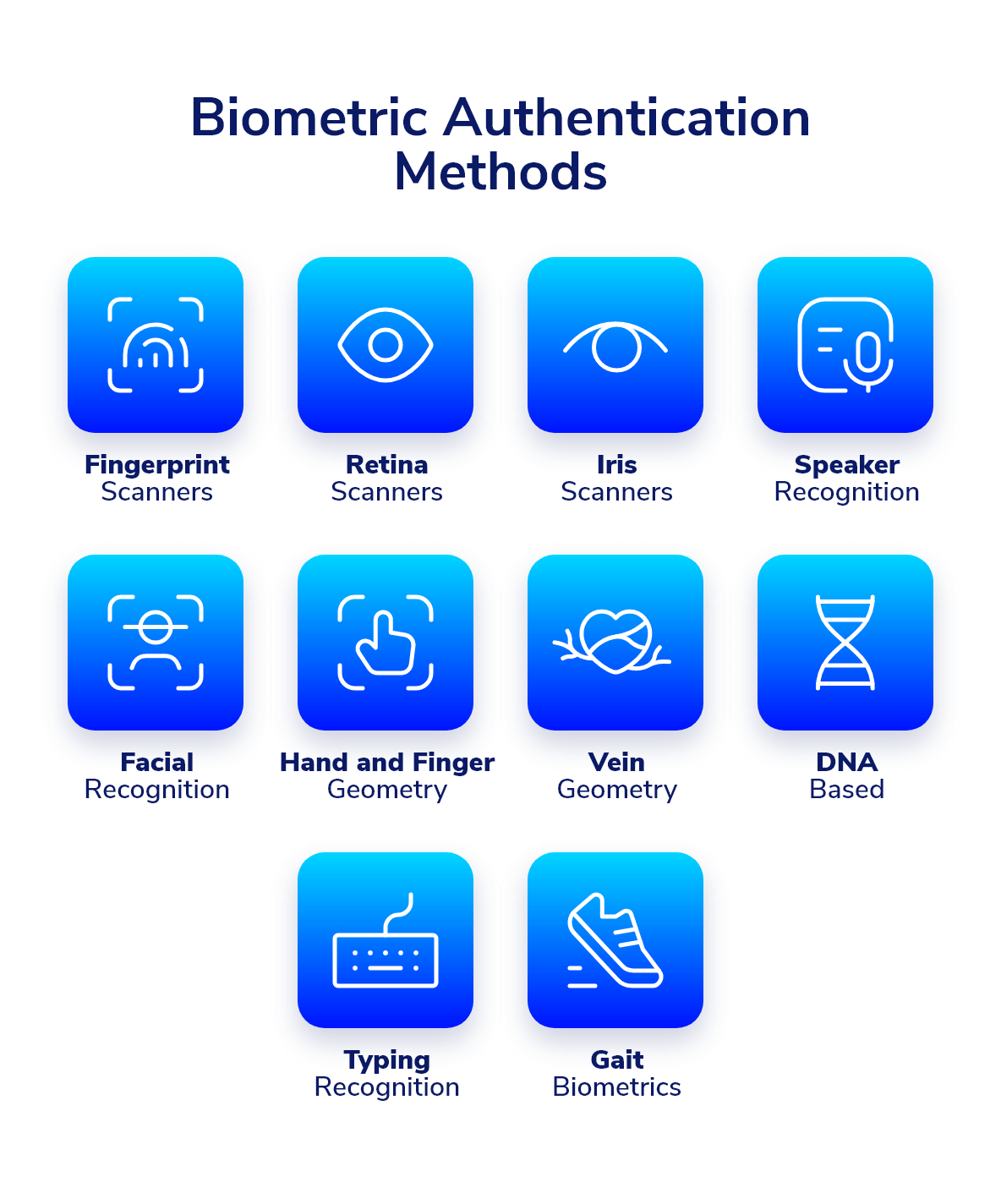
Types of Biometric Authentication
-
Fingerprint Recognition
- How it Works: Scans and analyzes the unique patterns of a person's fingerprint.
- Applications: Smartphones, laptops, access control systems, and time attendance systems.
-
Facial Recognition
- How it Works: Uses a camera to capture and analyze facial features, including the distance between eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Applications: Smartphones, security systems, and social media tagging.
-
Iris Recognition
- How it Works: Scans the unique patterns in the colored ring of the eye using infrared light.
- Applications: High-security areas, border control, and smartphone authentication.
-
Voice Recognition
- How it Works: Analyzes the unique characteristics of a person's voice, such as pitch, tone, and speech patterns.
- Applications: Call centers, voice-activated devices, and secure access systems.
-
Retina Scanning
- How it Works: Uses a low-intensity light source to scan the unique pattern of blood vessels in the retina.
- Applications: High-security areas, military installations, and government facilities.
-
Hand Geometry Recognition
- How it Works: Measures and analyzes the shape, size, and geometry of a person's hand.
- Applications: Access control systems and time attendance systems.
-
Behavioral Biometrics
- How it Works: Analyzes patterns in user behavior, such as typing rhythm, mouse movements, and usage patterns.
- Applications: Fraud detection, continuous authentication, and user behavior analysis.
Applications of Biometric Authentication
-
Mobile Devices
- Smartphones and tablets use fingerprint and facial recognition for unlocking devices and authorizing payments.
-
Banking and Finance
- Banks use biometric authentication for secure online banking, ATM access, and transaction approvals.
-
Access Control
- Biometric systems control access to buildings, rooms, and secure areas in organizations and government facilities.
-
Healthcare
- Ensures secure access to patient records, prescription approvals, and access to medical facilities.
-
Travel and Immigration
- Airports and border control use biometric systems for passport verification and secure border crossings.
-
Law Enforcement
- Identifies criminals, missing persons, and verifies identities in forensic investigations.
Benefits of Biometric Authentication
-
Enhanced Security
- Biometrics provide a higher level of security compared to traditional methods, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.
-
Convenience
- Users do not need to remember passwords or carry access cards; their unique biological traits serve as their credentials.
-
Accuracy
- Biometric systems offer high accuracy in identity verification, minimizing false positives and negatives.
-
Speed
- Fast and efficient authentication process, improving user experience and productivity.
-
Non-Transferable
- Biometric traits are unique to individuals and cannot be easily shared or duplicated.
Challenges and Concerns
-
Privacy Issues
- Concerns about the storage and use of biometric data and potential misuse by unauthorized parties.
-
Cost
- Implementation of biometric systems can be expensive, requiring specialized hardware and software.
-
False Positives/Negatives
- Although rare, biometric systems can sometimes incorrectly identify or fail to identify individuals.
-
Data Security
- Protecting stored biometric data from breaches and cyberattacks is crucial.
Future Trends
-
Integration with AI
- AI and machine learning enhance the accuracy and capabilities of biometric systems, providing more robust security solutions.
-
Multimodal Biometrics
- Combining multiple biometric modalities (e.g., fingerprint and facial recognition) for higher accuracy and security.
-
Wearable Biometric Devices
- Biometric sensors integrated into wearable devices for continuous authentication and health monitoring.
-
Blockchain for Data Security
- Using blockchain technology to secure and manage biometric data, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Conclusion
Biometric authentication systems represent the future of secure and convenient access control. By leveraging unique biological traits, these systems offer unparalleled security and user experience. As technology advances, biometric authentication will continue to evolve, integrating with emerging technologies to provide even more robust and reliable solutions. Embracing this innovation will not only enhance security but also streamline access to the digital and physical worlds.