SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
SEO is the process of optimizing your website to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) to increase organic (non-paid) traffic. Here are some key components and techniques:
On-Page SEO
- Keyword Research: Identifying the keywords and phrases that potential customers are searching for.
- Content Optimization: Creating high-quality, relevant content that targets those keywords.
- Meta Tags: Optimizing meta titles, descriptions, and headers with relevant keywords.
- Internal Linking: Linking to other pages on your website to improve navigation and help search engines understand the structure of your site.
- Image Optimization: Using alt tags and proper file names to help search engines index images correctly.
Off-Page SEO
- Backlinks: Acquiring links from other reputable websites to increase your site's authority.
- Social Signals: Promoting your content on social media to drive traffic and engagement.
- Guest Blogging: Writing articles for other websites to gain backlinks and exposure.
Technical SEO
- Site Speed: Ensuring your website loads quickly.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Making sure your site is optimized for mobile devices.
- XML Sitemaps: Creating sitemaps to help search engines index your site more effectively.
- Robots.txt: Using robots.txt files to manage how search engines crawl your site.
SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
SEM involves using paid advertising to increase visibility in search engine results pages. This typically refers to the use of pay-per-click (PPC) ads. Here are some key components:
PPC Advertising
- Google Ads: Running ads on Google’s search engine and its display network.
- Bing Ads: Running ads on Bing’s search engine.
- Keyword Bidding: Bidding on keywords relevant to your business to display your ads when those keywords are searched.
- Ad Copy: Writing compelling ad copy to attract clicks.
- Landing Pages: Creating optimized landing pages that convert visitors into customers.
Ad Types
- Search Ads: Text ads that appear at the top of search results.
- Display Ads: Banner ads that appear on websites within the Google Display Network.
- Shopping Ads: Product-based ads that appear in search results and on Google Shopping.
- Video Ads: Ads that appear on YouTube and other video platforms.
Performance Tracking
- Conversion Tracking: Monitoring the actions users take after clicking on your ad (e.g., purchases, sign-ups).
- Analytics: Using tools like Google Analytics to track and analyze the performance of your ads.
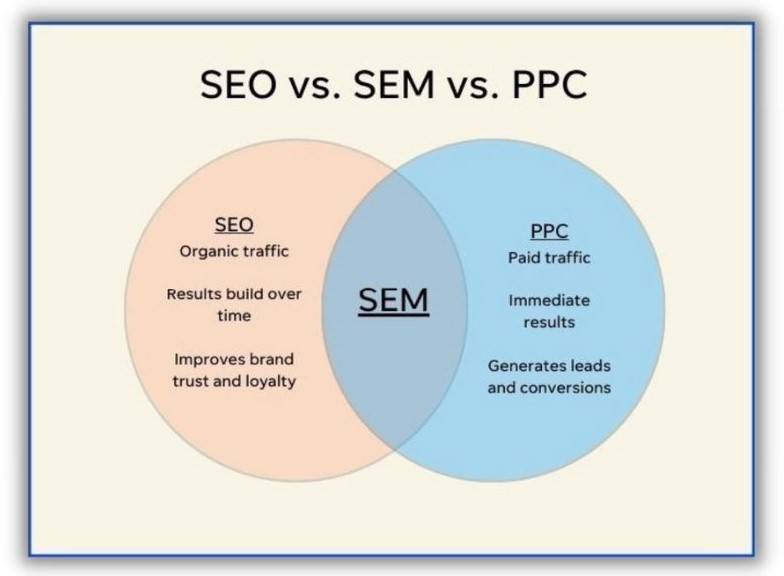
Differences Between SEO and SEM
- Cost: SEO focuses on organic traffic and doesn’t involve paying for clicks, while SEM involves paying for ads.
- Time: SEO is a long-term strategy that takes time to see results, whereas SEM can produce immediate results.
- Sustainability: SEO results can be more sustainable over time, as high-ranking pages can continue to attract traffic. SEM results last only as long as you pay for ads.
Combining SEO and SEM
- Comprehensive Strategy: Using both SEO and SEM can provide a comprehensive approach to increasing visibility and driving traffic.
- Data Insights: SEM can provide quick data on which keywords and ads perform best, which can then inform your SEO strategy.
- Immediate and Long-Term Results: SEM can drive immediate traffic while you build your organic presence through SEO.
By understanding and utilizing both SEO and SEM, businesses can effectively enhance their online presence and attract more potential customers.